Toward the end of last semester – after lengthy and vigorous and unflinching hacking of red tape – we offered the first workshop – Beer Science: Measuring Beer Bitterness – as part of our ongoing Fermentation Science efforts. We started the day in the Chemistry lab, where Max Mahoney (Chemistry professor and makerspace faculty champion) described the chemistry of beer, and led students through a procedure for measuring beer bitterness.
Here’s how Max describes it:
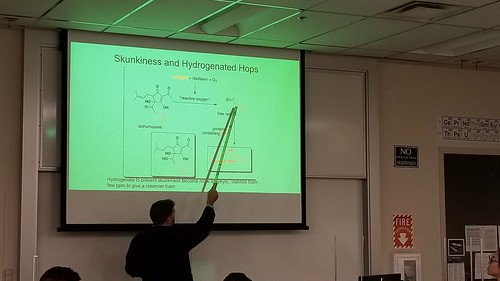
The goal of this workshop was to expose students to a quantitative and qualitative analysis of beer bitterness. The chemistry of hops and bittering compounds was presented along with a discussion of the chemical procedures involved in this analysis. The following procedure was used to quantitatively analyze beer bitterness. Three beers were selected containing different levels of the hop-derived bittering agents. Students sonicated the beer to expel carbon dioxide, performed a liquid-liquid extraction of the hop acids with iso-octane, and measured the UV and visible absorption spectrum for their sample. We used the visible absorption spectra to help classify the style of beer. The UV absorption was used to quantify the concentration of hop acids and thus the bitterness of the beer (measured in IBUs).
Chemistry students of all levels were able to learn advanced analytical methods used in the beverage industry to analyze beer bitterness. General and organic chemistry lab techniques were utilized including UV-Vis spectroscopy, usage of micropipettes, and liquid-liquid extraction of organic compounds.
The Chemistry lab portion completed, we went over to the Innovation Center for some blind taste tests. Students sampled various beers, and then used PollEverywhere to report the perceived bitterness of the sample, the results of which we compared to the lab-derived values.
The event was a terrific success, and students were engaged and enthusiastic. We’ve got additional interdisciplinary FermSci workshops and projects planned for this semester, including more beer chemistry, sauerkraut making, curriculum development, and a partnership with a local employer for integrating IOT technology into kombucha fermentation.